18.02.201915:25pm

posted by Christian Deiters
The term “ontology” originally comes from philosophy and means “doctrine of being”. Since the 1990s, it has also been used in IT research in the field of artificial intelligence where it designated formal representation systems. These serve to bring knowledge domains into a machine-readable form. An ontology describes a collection of concepts as well as the relationships in which these concepts relate to each other. Above all, it is about how to deal with ambiguous terms, the meaning of which is only discernible from the context. Take the word “jaguar”, for example. It must be clearly defined whether a term refers to feline predators or a car brand.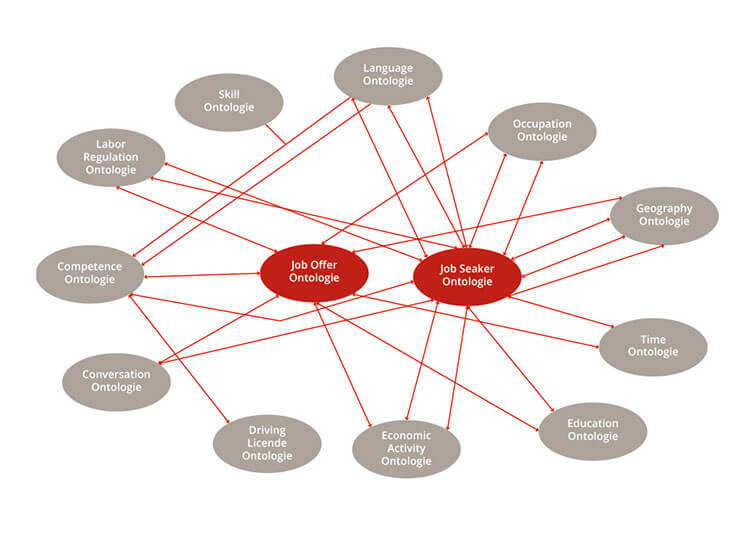 The main elements of an ontology are “classes” (concepts), “slots” (characteristics, attributes of a class as well as methods you can use with a class) as well as “individuals” (instances of a class). Like taxonomies, ontologies are also hierarchical in structure. In contrast, a subclass automatically inherits all the properties of the overlying class (superclass). In addition, an ontology records synonyms such as, for example, car, vehicle, motor, lorry, van, truck and links these together. The process to dispose of an ontology can be complicated and arduous. In addition to the purely content-related challenge, there are sometimes many people involved in modelling a knowledge domain. For example, just as the volume of data and the number of people involved increase, so does the difficulty of reaching an agreement.
The main elements of an ontology are “classes” (concepts), “slots” (characteristics, attributes of a class as well as methods you can use with a class) as well as “individuals” (instances of a class). Like taxonomies, ontologies are also hierarchical in structure. In contrast, a subclass automatically inherits all the properties of the overlying class (superclass). In addition, an ontology records synonyms such as, for example, car, vehicle, motor, lorry, van, truck and links these together. The process to dispose of an ontology can be complicated and arduous. In addition to the purely content-related challenge, there are sometimes many people involved in modelling a knowledge domain. For example, just as the volume of data and the number of people involved increase, so does the difficulty of reaching an agreement.

posted by : Christian Deiters